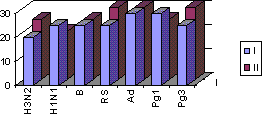"assert"
_____________________
I.A. of Leshkevich
Deputy Chairman K3 of Moscow
Report
on the theme
Study of epidemiological effectiveness in the application of domestic
preparation Of "arbidol" for preventive maintenance and treating the
sharp respiratory virus infections in Moscow
Executors: K.M.N. the docent of kaf. of infectious diseases RMAPO the chief epidemiologist KZ of the substitute of the head physician OF GKB of im.S.P. Botkin Sel'kova YE.P., the chief epidemiologist OF UZAO of g.Zelenograd of substitute. The head physician OF GKB № of 3 Gracheva I.YU., D.M.N., professor, the hands lab. of the unspecific preventive maintenance of the infectious diseases NIIEM of im.N.F.Gamalei IS FRAME T.A.Semenenko, K.M.N., S.N.S. T.P.Gotvyanskaya, N.S. Of M.P.Amaryan NIIEM of im.N.F.Gamalei IS FRAME
Moscow 2000-2001.
At present there does not exist vaccine preparations against the urgent agents of respiratory infections (with exception of influenza vaccines), which contributes to the maintenance of the morbidity of adult and children's population at the high level. In connection with this to completely regularly accentuate attention to the study of epidemiological effectiveness and the application of effective means of the unspecific preventive maintenance of sharp respiratory virus infections (ORVI).
One of the methods of solution of the problem indicated is the search for the preparations, which combine antiviral activity with the immunostimulating properties. Unspecific preventive maintenance is shown to people with the clinical signs of the decreased resistance of the organism: _ frequent respiratory disease with protracted or complicate flow; by the presence of the chronic centers of infections; by severe chronic somatical illnesses. Not is less urgent unspecific preventive maintenance ORVI among the contingents of the risk, which include medical workers, who are, in view of the specific character of their activity, those not only by most subjected to the risk of infection, but also the source of infection for the patients with respect to these infections.
The purpose of the present investigation was the study of the epidemiological effectiveness of the domestic preparation of arbidol, created in the Center for chemistry of medicines - All-Russian scientific research chemicopharmaceutical institute (VNIKHFI - ALL-UNION SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH CHEMICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL INSTITUTE IM. SERGO ORDZHONIKIDZE), and permitted Farmkomitetom MZ RF to the application in practical public health.
Materials and the methods
The preparation of arbidol (ethyl ether 6 - bromine - 5 - hydroxy - 1 - methyl - 4 - dimethylaminomethyl - 2 - phenylthiomethyl - indole - 3 - carbonaceous acid hydrochloride, monohydrate) in the form of tablets on 0.2 g used with the preventive purpose orally 2 times a week during the 3rd weeks.
The study of the influence of arbidol on immune status was conducted on the limited contingent of the medical workers TSKB №y of g.Zelenograda. By the method of the random sampling it was formed 2 equivalent in every respect of group of 38 people in each: the 1st - obtained arbidol (experimental); 2-4 - placebo according to the same diagram (control group). Research were conducted in the dynamics: prior to the beginning of the application of preparation (1 test), in 7 days (2 tests) and in 21 days (3 tests) from the beginning of the application of arbidol.
The immunomodulating activity of preparation was determined in accordance with the systematic recommendations regarding the estimation of immune status of man, by the developed colleagues of the institute of immunology MZ RF under the management of the academician OF RAN [RUSSIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCE] WAS FRAME R.V.Petrova. All persons in the experimental and control groups were inspected according to the united diagram, which included the study of the parameters, which reflect the functioning of basic it was sectional immune system (cellular, humoral and phagocytic): the determination of the number of leukocytes and lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes (CD3) and their subpopulations (CD4 and CD8), immunoregulator index (CD4/CD8), the content of B-lymphocytes (CD19), NK cells (natural killers -.cD16), immunoglobulins of basic classes, TSIK and indices of phagocytosis.
A serological study of the models of blood serum is carry out for the purpose of the evaluation of the influence of preparation on the indices of specific immunity. By the randomized method were formed 2 groups: I - (experimental) by the number of 96 people obtained arbidol; II - (control room) with the number of 107 people obtained placebo. Blood serum were investigated in the immunoenzyme analysis (IFA) to the presence of specific antibodies to the viruses of influenza A (H1N1 and H3N2) and in, to respiratory-syncytial (RS) virus, to adenovirus and to the viruses of parainfluenza of the 1st and 3rd types. With setting of reaction was used the test- system, which is the 13- component collection, basic components of which are the antigens of respiratory viruses, utilized for the absorption on the surface of the holes of polisterolovykh plane-tables, and also the conjugates of monoclonal antibodies to IgM and IgG man (production OF NII - SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH INSTITUTE influenza IT IS FRAME). The detection of specific complex antigen-antibody was produced with the aid of the marked by peroxidase monoclonal antibodies to IgM and IgG man.
The study of the epidemiological effectiveness of arbidol was conducted in the autumn-winter period of 2001-2002 on the contingent by the number of 2055 people. With the preventive purpose the preparation obtained 940 people (experimental group), 1115 people obtained placebo (control group).
For the duration entire of the period of observation the persons included in epidemiological experience find under a constant clinico- epidemiological observation with the required registration of all cases of infectious diseases. With the special attention they related to registration and inspection sick ORVI, actively they revealed the persons with the signs of respiratory infections.
The preparations (arbidol and "placebo") used was subject to coding. The ciphers of the obtained preparations were fixed in the special "maps of the inspection", brought on all included in experience persons.
Map of the inspection
F.I.O....................................... Age........................
Dom.adres................................. Telephone........................
General state of organism prior to the beginning of treatment
by...........................
..........................................................................................
Associated diseases by...................................................
Each case of disease in the required order was considered in the "map of the inspection" of sick person and was recorded in the routine in the public health station LPU, and also in the corresponding divisions of the calculation of the leaves of disablement. For studying of level and dynamics of infectious morbidity in the experimental and control groups the information was selected of the documents enumerated above. The selected from the accounting forms primary cases of infectious diseases grouped depending on the cipher, carried into the "map of inspection".
For studying the dynamics of morbidity ORVI, furthermore, was produced the group of diseases on ten-day-periods and months of observation. The absolute number of cases of diseases in the experimental and control groups was transferred into the intensive indices (number of sick people to 1000 people), after which was conducted the calculation of measures of effectiveness, and also the determination of the authenticity of differences in the levels of morbidity in the experimental and control groups.
All quantitative indices were processed by the methods of variation statistics. The authenticity of differences was determined on Student's t- criterion, in this case by statistically reliable were considered the differences with r < 0.05.
Results
The study of the epidemiological effectiveness of arbidol was conducted in the autumn-winter period of 2001-2002 on the contingent by the number of 2055 people. With the preventive purpose the preparation obtained 940 people (experimental group), 1115 people obtained placebo (control group).
For the purpose of the study of the epidemiological effectiveness of the preparation of arbidol with respect to the group of respiratory virusoov were carry out the serological studies, which revealed the presence of the wide spectrum of the agents, which circulated in the period of conducting epidemiological tests. In contrast to previous, into the season 2001-2002 etiological structure ORVI underwent some changes, represented in the table.
Etiological structure ORVI among the persons, included in epidemiological experience on the application of arbidol
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
So, the greatest specific weight to zabolevayemsoti ORVI both in the persons of experimental and control room of groups was caused by adenovirus (22.3±3.3% and 19.5±1.8%) and by RS- virus (15.0±2.1% and 15.8±2.2%) respectively. The participation of the viruses of parainfluenza in the etiology ORVI was considerably less than in the previous years composed for parainfluenza 1 types 3.3±0.5% (experimental group), 6.6±0.8% (control group) and for 3 types parainfluenza 5.9±0.7% and 4.9±0.4% respectively.
Specific weight of the mono- and mixed infection in the etiology ORVI in the experimental and control groups
|
the experimental group |
the control group |
|
|
|
The important significance have results of a study regarding in those investigated of the presence of antibodies, that characterize their infection, represented in the figure. Thus, the simultaneous diagnostic determination of the captions of antibodies to two or more infectious agents, included in a study, are noted into 43.7 ± by 5.1% (experimental group) and 52.2 ± 5.4% of cases control group).
The specific weight of the separate exciters, which enter in the association, was unequal and depended on the intensity of their circulation in the period of inspection. The most frequent "partners" with the formation of the mixed infections both in the experimental and control group were the viruses of 1 types parainfluenza (27.8 ± 5.5% and 25.6 ± 4.1%) and adenoviruses (18.8 ± 3.6% and 18.4 ± 2.3%). Frequently they were encountered in the association the virus of influenza A (H3N2) (9.5 ± 2.6% and 10.3 ± 1.7%) and the virus of 3 types parainfluenza (6.9 ± 2.6% and 7.8 ± 1.2% respectively) (Fig.)
Dynamics of the captions of specific antibodies in the healthy persons, who obtained arbidol or placebo
|
|
The carried out epidemiological tests (tablitsa)pokazali, that the application of arbidol led to the expressed reduction in the morbidity by influenza and ORVI in the persons of experimental group in comparison with the control room.
|
||||||||||||||
The determination of the measures of the effectiveness of arbidol with respect to the large group of respiratory viruses confirmed its high preventive activity. The index of effectiveness with respect to the viruses, which cause sharp respiratory infections, in the experimental group composed 3.2 with the appropriate index of protection - 68.7%.
In all likelihood, the preventive effect of arbidol can be above in the period of the epidemics of influenza. Thus, according to the data NII - SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH INSTITUTE influenza IS FRAME, the application of preparation among the working industrial enterprises of g.Severodvinska during the epidemic of an influenza of the type A led to reduction in the morbidity 3.8 times. Is shown also the high preventive effectiveness of arbidol during its application in those, who contacted with the patients with influenza in the period of the epidemic outbreaks of influenza A also in, the exceeded effectiveness of remantadine. The index of the effectiveness of arbidol with respect to the placebo composed 6.7, and with respect to remantadine 4.5 with the corresponding indices of protection 85.1% and 77.8%.
Our studies were carry out in the conditions for the seasonal lift of morbidity ORVI, but not against the background of the epidemic of influenza. Is expedient further conducting of studies among different contingents into the interseasonal and into the periods of the highest lift of morbidity by influenza and ORVI.
The conducted investigations showed that arbidol renders the immunomodulating action, leading to an increase in the total quantity of T-lymphocytes and T- helpers, which was determined with the aid of the monoclonal antibodies to the antigens of lymphocytes (table 1).
Table 1
Absolute content of T-lymphocytes and T- helpers in the dynamics of observation
(in the persons of experimental and the control room of groups)
|
||||||||||||
It should be noted that in this case the discussion deals with the normalization of indices in the persons with initially decreased number CD3 and CD4 cells, and practically by the absence of influence on the total quantity of T-lymphocytes and T- helpers in the inspected medical workers with the normal functioning of the cellular component of immunity. These data will agree with the results, obtained earlier in the limited experiences by other authors.
At the same time the application of preparation did not lead to substantial changes of the absolute number of T- suppressor cells as a whole on the groups (tabl.2), which confirms the opinion of the number of researchers about the fact that arbidol stimulating activity is not connected with the oppression of the function of suppressor cells (10).
Table 2
Absolute content T -supressorov in the dynamics of observation (in the persons
of experimental and the control room of groups)
|
||||||||
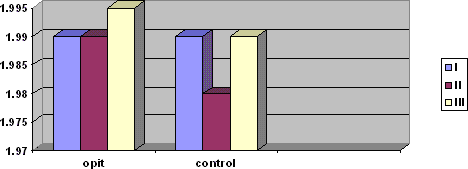
Determination of immunoregulator index (relationship of T- helpers/T -supressorov) also gives important information about the state of the immunity of man, since his decrease testifies about development or presence of immunodeficient state, and a sharp decrease (to 0.5 - 0.6) is possible with AIDS. Obtained by us data testify about the absence of the influence of amiksina on the immunoregulator index, which is located within the limits of standard, and its normalization in 11- TI of men with the initially decreased indices (Fig.).
Values of immunoregulator index in the
persons of experimental and the control room of groups in the dynamics of the
observation
On the X-axis - experimental and control room of group; on the Y-axis - value
of immunoregulator index.
|
|
The important property of arbidol is its stimulating influence on the phagocytosis. In the experiments carried out earlier on animals it was shown that the preparation not only increases the total number of macrophages with the absorbed bacteria, but also increases the phagocytic number. Strengthening phagocytosis is noted in patients, who suffer chronic bronchitis, which was accompanied by an improvement in the clinical state of the sick and in a number cases it made it possible to forego the method of antibiotics. In the conducted by us investigations confirmed stimulating action arbidol on the phagocytic component of immunity, which ensures an increase in the stability of macroorganism. The determination of the phagocytic activity of neutrophils made it possible to establish substantial changes in the indices in the persons of experimental group in comparison with the control room, about which testifies statistically a reliable increase in the phagocytic index in those, who obtained arbidol, with II and THE III inspection (t > 3) (table 3).
Table 3
Phagocytic index in the persons of experimental and the control room of groups
in the dynamics of the observation
|
||||||||||||
* r < 0.05 and ** r < 0.01 -
authenticity inside the group;
+r < 0.05 - authenticity between the groups.
In all likelihood, the activating stimuli for the phagocytic cells in the persons of experimental group were tsitokiny and, in particular, interferon, whose production is strengthened under the action of arbidol (4). With the analysis of the dynamics of the indices of natural killer activity the increase in content of NK- cells in the persons of experimental group, especially expressed during the second period of inspection was noted (table 4).
Table 4
Content NK of cells in the blood serum of those, who obtained arbidol and
placebo
|
||||||||||||||
* r < 0.05 - authenticity inside the
group;
+r < 0.05 - authenticity between the groups.
In contrast to the control room, in the experimental group with the defined fluctuations of the initial levels NK of cells the difference in the indices to (11 ± 0.9%) and after the method of arbidol with THE II inspection (16 ± 1.1%) and THE III inspection (13 ± 1.2%) was significant and statistically reliable (t>3, r<0.0shch), which makes it possible to characterize preparation as the inductor of the activity of natural killers.
In the process of conducting studies it was impossible to establish the essential influence of preparation on the content of B-lymphocytes and the levels of the immunoglobulins of basic classes.
Thus, the results of the conducted investigations attest to the fact that arbidol possesses the immunomodulating activity, which is manifested in an increase in the total quantity of T-lymphocytes and T- helpers, stimulation of the phagocytic function of neutrophils and induction of the activity of natural killers. Preparation does not render the immunosuppressing effect on the production of specific antibodies to the respiratory viruses, which profitably distinguishes it from the majority of the antiviral means, which are adapted for preventive maintenance and treating of influenza and ORVI.
The preformed form of preparation makes it possible to use it in the dispensary- polyclinical network for the mass preventive maintenance in the period of seasonal and mass lift.